Unlike regular variables, pointer variables do not store actual values; instead, they hold the memory addresses of other variables. Due to this, the arithmetic operations that can be performed on pointers are limited and differ from standard mathematical operations.
Increment/Decrement of a Pointer
Addition of integer to a pointer
Subtraction of integer to a pointer
Subtracting two pointers of the same type
Comparison of pointers
increment/decrement of a pointer:
int *ptr;
Ptr++;
Ptr–;
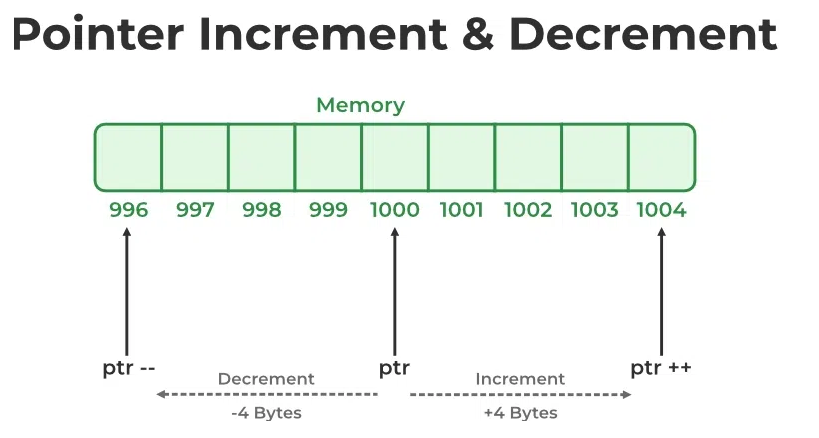
If the base address is 5000
Ptr++=5000+4;
Ptr–=5000-4;
For example if the base address is 5000 the ptr++=5004
And ptr–=5000-4=996;
Addition of integer to a pointer:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a=22;
char b=’a’;
int c[]={1,2,3,4,5};
float d=12.22;
int *p=&a;
char *q=&b;
int *r=&c;
printf(“%d integer ptr increment”,p++);
printf(“%d integer ptr decrement “,p–);
printf(“%d char ptr increment”,q++);
printf(“%d char ptr decrement”,q–);
printf(“%d array pointer increment “, r++);
printf(“%d array pointer decrement”,r–);
printf(“%dfloat pointer increment”,d++);
printf(“%dfloat pointer decrement”,d–);
}
Addition of integer to a pointer:
// C program to illustrate pointer Addition
#include <stdio.h>
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Integer variable
int p= 4;
// Pointer to an integer
int *p1, *p2;
//
p1 = &N;
p2 = &N;
printf(“Pointer ptr2 before Addition: “);
printf(“%p \n”, p1);
// Addition of 3 to ptr2
p2 = p2 + 3;
printf(“Pointer ptr2 after Addition: “);
printf(“%p \n”, p2);
return 0;
}
- Subtraction of Integer to Pointer:
#include <stdio.h>
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Integer variable
int p= 4;
// Pointer to an integer
int *p1, *p2;
//
p1 = &p;
p2 = &p;
printf(“Pointer ptr2 before Addition: “);
printf(“%p \n”, p1);
// Addition of 3 to ptr2
p2 = p2 – 3;
printf(“Pointer ptr2 after subtraction: “);
printf(“%p \n”, p2);
return 0;
}
Subtraction of two pointers:
// C program to illustrate Subtraction
// of two pointers
#include <stdio.h>
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int x =6;
int N = 4;
// Pointer declaration
int *p1, *p2;
p1 = &N;
p2 = &x;
// %p gives an hexa-decimal value,
// Subtraction of ptr2 and ptr1
x = p1 – p2;
// between ptr1 and ptr2
printf(“Subtraction of p1 “
“& p2 is %d\n”,
x);
return 0;
}
-We can compare the two pointers
-with the comparison operators.
< ,>,<=,>=
// C Program to illustrare pointer comparision
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
// declaring array
int a[5];
// declaring pointer to array name
int* p1 = &a;
// declaring pointer to first element
int*p2 = &a[0];
if (p1 == p2) {
printf(“
Equal.”);
}
else {
printf(“
“are not Equal.”);
}
return 0;
}


