At the core of every electronic device, printed circuit boards (PCBs) act as the essential platform for mounting electronic components, facilitating the creation of printed circuit board assemblies (PCB-A).
Why are they crucial for every electronic device, and what materials constitute their composition?
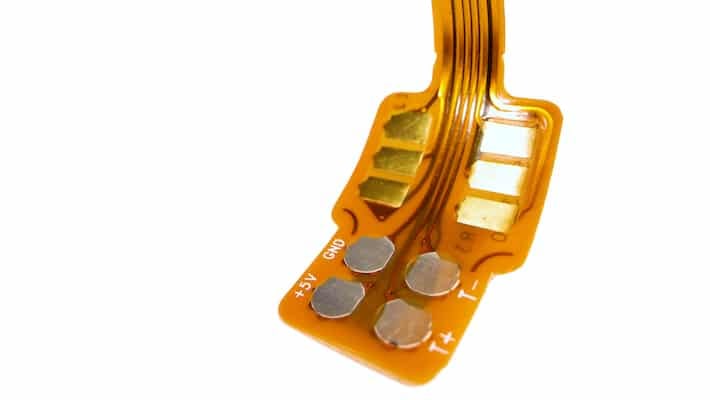

PCBs are not exclusively green; they can be found in various types and colors. This particular example is a flexible board.
What is a printed circuit board?
Essentially, a printed circuit board consists of non-conductive materials, including fiberglass or epoxy, that serve to mechanically support and electrically interconnect electronic components via conductive pathways that are either etched or printed onto the board’s surface. The method of building a circuit board can differ significantly depending on the type of board being used. In a multilayer PCB, multiple conductive layers of copper, typically three or more, are separated by layers of insulating material. The connection of components is achieved through tracks and pads within these layers.
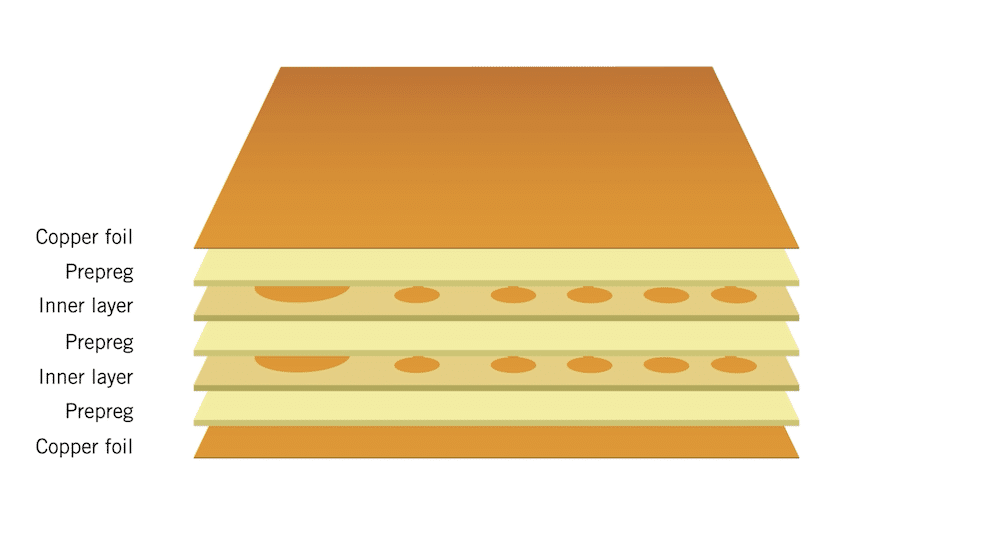 Illustration of a multilayer PCB
Illustration of a multilayer PCB
An additional illustration is the HDI PCB, which is characterized by IPC-2226 as a printed circuit board that exhibits a greater wiring density per unit area compared to traditional circuit boards. The technology features narrower lines and spaces measuring ≤ 100 µm / 0.10mm, smaller vias of less than 150 µm, and capture pads that are under 400 µm / 0.40mm, along with a greater density of connection pads exceeding 20 pads/cm2 compared to traditional PCB technology. Printed circuit boards serve as a foundation for mechanical support while facilitating electrical connections for various components, including resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits.
Compact yet crucial
The total value of the end product includes only a small fraction attributed to printed circuit boards. Nevertheless, these components are indispensable and fundamental to the overall product; addressing issues with a defective PCB can frequently be quite costly. For our customers, the significance of quality and reliability ranks high among their purchasing criteria.
Initially, the printed circuit boards might look comparable, no matter the variations in their quality. Yet, there are important discrepancies that affect both the durability and operational efficiency of the PCB throughout its lifespan. The distinction between a standard PCB and a dependable PCB can be significant. It lies in the attention to detail and the level of precision involved.
There are multiple types of circuit boards available, each tailored to address specific requirements and preferences concerning functionality, flexibility, and performance. Understanding that each PCB design is one-of-a-kind is crucial; these are not generic items. Instead, they are thoughtfully engineered to serve a specific purpose that no other design can achieve.
Furthermore, the expectations for the PCB are highly dependent on the industry and application, leading to considerable variations in its demands. Additionally, there are several standards that must be observed.
- Aerospace
- Automotive
- Datacom
- Defense
- Industrial
- Medical
- Power/energy
- Railway
- Safety critical
- Telecom
To be conclude
The pcbs are playing a vital role in electronics/Embedded systems and other sectors as mentioned above. So if possible everyone should know some basics of pcb.


 Illustration of a multilayer PCB
Illustration of a multilayer PCB