Preface
The RS232 standard governs the serial communication process, enabling data transmission between different types of devices. Originating in the 1960s, this interface standard is recognized as one of the oldest used in the field of computing. RS232 has been extensively utilized for establishing connections between devices like printers, modems, and various peripherals and computers. In spite of the introduction of newer interface standards, RS232 remains prevalent in a variety of industrial and commercial applications.
The system applies a voltage level shift to separate bits from bytes in the data stream. RS232 voltage levels are conventionally defined as +15 volts and -15 volts, where a positive voltage corresponds to logic 0 and a negative voltage corresponds to logic 1. Information is conveyed in a bit-by-bit fashion, with a complete byte made up of a start bit, the data bits, a parity bit, and a stop bit.
Equipment Specifications and Connection Interfaces
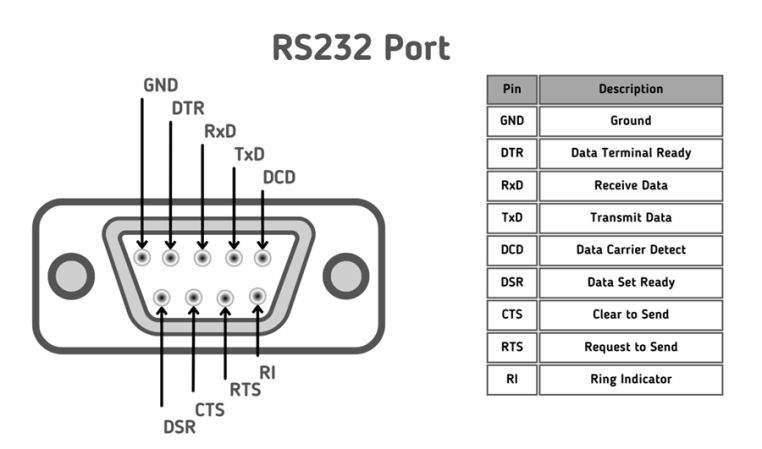
The electrical characteristics of the signals employed for communication are detailed in the hardware specification of RS-232. Data can be transmitted at a peak speed of 115200. The key types of connectors employed include DB-25 and DB-9. Featuring 25 pins, the DB-25 connector is designed for data transmission and reception, with the possibility that not every pin is employed. Similarly, the DB-9 connector includes 9 pins. The ports are divided into two types: male connectors (DTE) and female connectors (DCE), collectively referred to as D-type connectors.
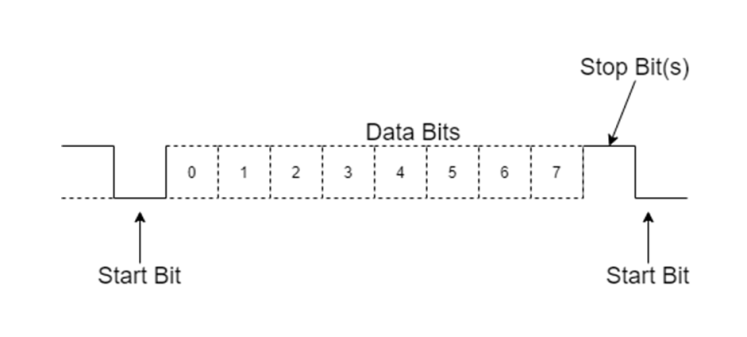
RS232 data packet Structure
The RS232 standard outlines the electrical, mechanical, and timing specifications for serial communication between devices, utilizing a UART packet format for the transfer of data. The format of this packet comprises a start bit, data bits, an optional parity bit, and stop bits, commonly employed in UART communication.
The RS232 standard utilizes voltage levels to signify binary data, assigning a positive voltage to represent a logical 0 and a negative voltage to represent a logical 1. The defined voltage levels are intended to provide consistent communication over longer distances, extending to 50 feet or greater.
HandShake
In the context of RS-232 communication, handshake denotes the procedure in which two devices validate their availability and readiness to transfer data between them. This method confirms that both devices are adequately prepared for data transmission and reception, which significantly reduces the likelihood of information loss or damage during the process.
The Request to Send (RTS) and Clear to Send (CTS) signals are the most frequently employed handshake signals in RS-232 communication. Upon readiness to send data, a device transmits an RTS signal to the receiving device, which indicates that it is seeking authorization to initiate the transmission. A CTS signal is generated by the receiving device, indicating that it is prepared to receive data. The transmitting device is permitted to commence data transmission once it has received the CTS signal.
RS232 Applications
The RS232 standard has been extensively adopted in previous years for linking computers to devices such as printers, modems, and other peripheral equipment. This technology has found applications in industrial and commercial fields, particularly in data acquisition and control, process control systems, and the automation of manufacturing processes. Despite the introduction of newer interface standards such as USB and Ethernet, RS232 remains prevalent in various industrial and commercial applications today.
In closing
RS232 serves as a standard protocol for the serial transmission of data between multiple devices. It has long been a prevalent method for connecting devices, including printers, modems, and other peripherals to computers, and it is still actively used in a variety of industrial and commercial applications today. RS232 is an uncomplicated and trustworthy communication standard that has demonstrated its longevity, and it is likely to persist in usage for many years to follow.



