Why Timers and Counters in 8051 Are Important
The importance of timers and counters in 8051 goes beyond academic learning.
In real embedded products, accurate timing control is essential.
A well-configured 8051 timer allows engineers to synchronize tasks,
generate delays, and respond to external events.
Key reasons why timers and counters in the 8051 microcontroller are important include:
- Accurate time delay generation
- Counting external events such as pulses from sensors
- Baud rate generation for serial communication
- PWM signal generation
- Frequency measurement
- Real-time control applications
Because of these wide-ranging uses, 8051 timer programming is considered a core skill for embedded engineers.

Timer Mode vs Counter Mode in 8051
A crucial topic while learning timers and counters in 8051 is understanding the difference between timer mode and counter mode,
commonly referred to as timer vs counter in 8051.
Timer Mode
In timer mode, the 8051 timer increments based on the internal clock.
This internal clock is derived from the oscillator frequency in 8051,
divided by 12 to form the machine cycle.
Timer mode is mainly used for delay generation and baud rate control.
Counter Mode
In counter mode, the 8051 timer and counter increment based on external pulses applied to the T0 or T1 pins.
The counter increments on each high-to-low transition of the input signal.
This mode is useful for counting events such as object detection or RPM measurement.
Understanding timer vs counter in 8051 is essential for selecting the correct mode during 8051 timer programming.

Timer Registers in the 8051 Microcontroller
The operation of timers and counters in the 8051 microcontroller is controlled using 8051 special function registers (SFRs).
These registers allow programmers to configure modes, start or stop timers, and monitor overflow conditions.
TCON Register in 8051 (Timer Control Register)
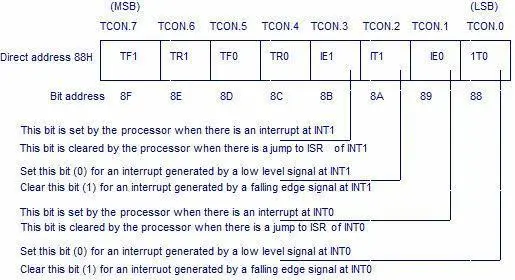
The TCON register in 8051 controls the execution and status of Timer 0 and Timer 1.
| Bit | Name | Description |
|---|
| TF1 | Timer 1 Overflow Flag | Set when Timer 1 overflows |
| TR1 | Timer 1 Run Control | Starts or stops Timer 1 |
| TF0 | Timer 0 Overflow Flag | Set when Timer 0 overflows |
| TR0 | Timer 0 Run Control | Starts or stops Timer 0 |
A strong understanding of the TCON register in 8051 is mandatory for accurate 8051 timer programming.
TMOD Register in 8051 (Timer Mode Register)
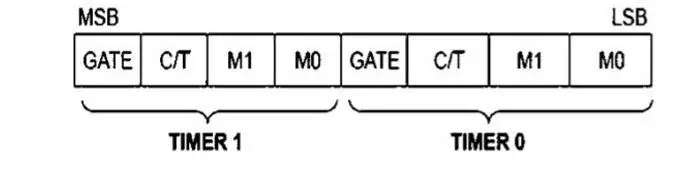
The TMOD register in 8051 selects the operating mode of timer 0 and timer 1 in 8051.
| Bits | Function |
|---|
| M1, M0 | Select timer mode |
| C/T | Timer or counter selection |
| GATE | Gated or free-running operation |
The TMOD register in 8051 works together with the TCON register in 8051
to fully configure timers and counters in 8051.
THx and TLx Registers
The actual count values of timers and counters in 8051 are stored in the THx and TLx registers.
- TH0 and TL0 → Timer 0 high and low byte
- TH1 and TL1 → Timer 1 high and low byte
These registers directly affect delay accuracy and timing precision.
Modes of Timers and Counters in 8051
Mode 0 – 13-Bit Timer Mode
- Uses a 13-bit counter
- Rarely used in modern designs
Mode 1 – 16-Bit Timer Mode
- Full 16-bit operation
- Maximum count: 65,535
- Used for long delays
Mode 1 is the most widely used mode in 8051 timer programming
and is central to understanding timers and counters in the 8051 microcontroller.
Mode 2 – 8-Bit Auto Reload Mode
- TLx functions as an 8-bit counter
- THx stores reload value
- Automatically reloads after overflow
This mode is commonly used for baud rate generation in serial communication.
Mode 3 – Split Timer Mode
- Available only for Timer 0
- Splits Timer 0 into two independent 8-bit timers
- TH0 uses Timer 1 control bits
Example: Delay Generation Using Timer 0 (Mode 1)
ORG 0000H
MOV TMOD, #01H ; Timer 0, Mode 1
HERE:
MOV TL0, #0F2H
MOV TH0, #0FFH
SETB TR0
WAIT: JNB TF0, WAIT
CLR TR0
CLR TF0
SJMP HERE
END
This example is widely used in laboratories to demonstrate timers and counters in 8051.
Worked Numerical Example – Delay Calculation
To further understand timers and counters in 8051, consider the following calculation.
Given:
Oscillator frequency = 11.0592 MHz
Machine cycle = 1.085 µs
Required delay = 10 ms
Total counts required:
10 ms / 1.085 µs ≈ 9216 counts
Initial value:
65536 − 9216 = 56320 = DC00H
Load:
TH0 = DCH
TL0 = 00H
This example highlights the importance of oscillator frequency in 8051 during 8051 timer programming.
Common Mistakes in Timers and Counters in 8051
- Forgetting to clear TF0 or TF1
- Incorrect TMOD register configuration
- Wrong initial values in THx and TLx registers
- Confusion between timer and counter mode
- Using incorrect crystal frequency
Avoiding these errors improves reliability in 8051 timer and counter applications.
Applications of Timers and Counters in 8051
- Digital stopwatches
- Real-time clocks
- PWM motor control
- Frequency counters
- Serial communication timing
8051 Timer vs AVR Timer
While learning timers and counters in 8051, students may also encounter the AVR timer.
An AVR timer offers advanced features, but the 8051 timer remains an excellent learning platform
for understanding fundamental timing concepts.
Why Learn Timers and Counters in 8051 at IIES
To truly master timers and counters in 8051, hands-on training is essential.
IIES (Indian Institute of Embedded Systems) offers the best embedded course in Bangalore, providing:
- In-depth 8051 timer programming
- Practical hardware labs
- Embedded C and Assembly training
- Interview-focused curriculum
This structured approach helps students gain confidence in timers and counters in the 8051 microcontroller.

Conclusion
Timers and counters in the 8051 microcontroller play a vital role in embedded systems design. By configuring the TMOD, TCON, THx, and TLx registers, engineers can generate precise delays, count external events accurately, and manage time-critical tasks efficiently. Mastering timers and counters in 8051 through professional training at IIES, the best embedded course in Bangalore, builds a strong foundation for a successful embedded systems career.