Difference Between ASIC and FPGA – Core Concept
The difference between ASIC and FPGA is flexibility. An ASIC is a fixed-function chip manufactured for one specific task. Once fabricated, its hardware cannot be changed. An FPGA, on the other hand, is reprogrammable hardware that can be updated again and again using a bitstream. Every VLSI student in Bangalore must clearly differentiate fpga vs asic vs soc before stepping into the semiconductor industry.
ASIC Design Flow – From RTL to Silicon
The ASIC design flow is long but gives the highest performance and lowest power.
- Requirement specification
- RTL design in Verilog / VHDL
- Logic synthesis
- Physical design – placement and routing
- Tape-out and fabrication
- Post-silicon testing
Before any silicon tape-out, product teams always discuss fpga vs asic vs soc trade-offs to reduce risk.

FPGA Architecture – Why It Is So Flexible
The FPGA architecture consists of:
- Look-Up Tables (LUTs)
- Flip-flops
- Programmable interconnects
- DSP blocks and BRAM
Because of this structure, the comparison of fpga vs asic vs soc becomes critical for startups who need fast validation.
FPGA Design Flow – From Code to Bitstream
The FPGA design flow is very fast compared to ASIC.
- RTL design
- Synthesis
- Place and route
- Bitstream generation
- Programming
When time-to-market is important, engineers prefer fpga vs asic vs soc-based FPGA development.

SoC Architecture – Backbone of Embedded Products
The SoC architecture integrates CPU cores, memory controllers, I/O peripherals and accelerators on a single chip. This is why SoC in embedded systems powers smartphones, automotive ECUs and IoT devices. For embedded engineers, fpga vs asic vs soc is not a theory topic – it is a daily design decision.
FPGA vs ASIC – Performance and Power
| Parameter | FPGA | ASIC |
|---|
| Performance | Medium | Highest |
| Power | Higher | Lowest |
| Flexibility | High | None |
Every real product design review revolves around fpga vs asic vs soc trade-offs.
FPGA vs ASIC vs SoC – Final Comparison
| Feature | FPGA | ASIC | SoC |
|---|
| Flexibility | High | None | Software controlled |
| Initial Cost | Low | Very high | High |
| Performance | Medium | Very high | Balanced |
| Use Case | Prototyping | Mass production | Embedded products |
Students preparing for interviews must clearly understand fpga vs asic vs soc using this table.
FPGA vs ASIC vs SoC – Architecture Diagram Explanation
FPGA Block Diagram
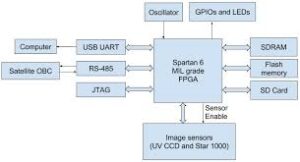
- Contains LUTs, flip-flops, DSP blocks and programmable routing fabric.
- This is why fpga vs asic vs soc discussions always start with FPGA prototyping.
- Used heavily in R&D, validation and pre-silicon verification.
ASIC Block Diagram
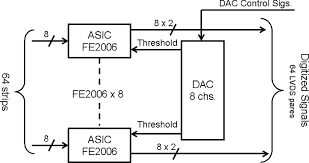
- Shows fixed-function hardware with no reprogrammability.
- Once fabricated, logic cannot be changed.
- Best choice in fpga vs asic vs soc when power, speed and high-volume production matter.
SoC Block Diagram
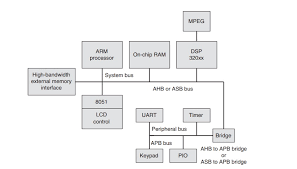
- Integrates CPU core, memory controller, I/O peripherals and accelerators.
- Backbone of SoC in embedded systems such as smartphones, automotive ECUs and IoT devices.
- Modern RISC-V SoC platforms follow this exact architecture.
Real Industry Case Study – Bengaluru Startup
A Bengaluru startup building a smart-camera initially selected fpga vs asic vs soc using FPGA to validate their image-processing pipeline. After customer traction, they moved to ASIC to reduce power consumption and per-unit cost. Finally, they integrated the design into a custom SoC for their embedded product. This practical use of fpga vs asic vs soc saved them more than 8 months of redesign effort.
Semicon India & Made-in-India Chips
Under the Semicon India program, startups are building Made-in-India chips using FPGA prototypes, ASIC accelerators and open-source RISC-V SoC platforms. The future of Indian semiconductor design depends heavily on mastery of fpga vs asic vs soc. At IIES – the best VLSI institute in Bangalore, students work on real FPGA, ASIC and SoC-based projects aligned with this ecosystem.
FPGA vs ASIC vs SoC – VLSI Interview Questions
Entry-Level Questions
- What is the basic difference between ASIC and FPGA?
- Explain FPGA architecture.
- What is SoC architecture?
- Why is SoC in embedded systems popular?
Mid-Level Questions
- Explain the ASIC design flow.
- Compare FPGA vs ASIC in terms of power and performance.
- Why is FPGA used before ASIC fabrication?
- What is RISC-V SoC?
Experienced-Level Questions
- When should a product migrate from FPGA to ASIC?
- How do timing-closure challenges differ in FPGA and ASIC?
- How do you select between fpga vs asic vs soc in a Made-in-India chip project?








