1. Lack of True Understanding and Conscious Awareness
One of the most fundamental Artificial Intelligence limitations is the lack of genuine understanding.
AI systems can analyze text, images, audio, and sensor data at incredible speed. Language models can generate fluent sentences, answer questions, and even write code. But none of this means AI understands what it is doing.
AI does not grasp:
Instead, it operates through:
- Data correlations
- Mathematical optimization
- Learned statistical patterns
Humans, in contrast, interpret information using context, experience, and intuition. This gap becomes especially visible in complex or ambiguous situations.
In engineering, embedded systems, and safety-critical applications, understanding context is just as important as executing logic. Even a small misinterpretation can lead to serious consequences something AI systems are not yet equipped to handle independently.

2. Emotional Intelligence and Human Empathy
Emotional intelligence involves recognizing emotions, understanding emotional context, and responding with empathy. This ability develops through life experience, social interaction, and cultural awareness.
AI can be trained to:
- Detect facial expressions
- Analyze voice tones
- Identify emotional keywords
But it cannot:
- Truly feel emotions
- Understand emotional depth
- Empathize with lived human experiences
For example, AI may detect that a person sounds upset, but it does not understand why they feel that way or how those emotions relate to past experiences. This limitation is especially evident in counseling, education, leadership, healthcare, and customer support.
AI can assist humans, but it cannot replace the emotional connection that only people can provide.
3. Absence of Common Sense Reasoning
| Aspect | Human Intelligence | Artificial Intelligence |
| Understanding | True comprehension and awareness | Pattern-based data processing |
| Emotional Intelligence | Empathy, intuition, emotional depth | Emotion detection without understanding |
| Common Sense Reasoning | Natural and intuitive | Limited, data-dependent |
| Creativity | Original and innovative thinking | Recombines existing data |
| Ethical Judgment | Moral reasoning and accountability | Rule-based decisions |
| Physical Dexterity | Highly adaptive and precise | Limited to controlled environments |
| Learning Style | Experience-driven learning | Data-driven training |
Humans rely heavily on common sense, basic, intuitive knowledge about how the world works. We use it subconsciously in almost every decision.
For instance, humans naturally understand that:
- Objects fall when dropped
- People act with intentions
- Language often includes metaphors and implied meanings
AI struggles with this form of reasoning because common sense knowledge is rarely written explicitly in data.
Consider this example:
- A human understands “the system crashed” as a software failure
- An AI system might interpret it as a physical accident without proper context
In real-world engineering and embedded systems, common sense reasoning is essential for:
- Debugging complex issues
- Assessing safety risks
- Making system-level decisions
This remains one of the most challenging Artificial Intelligence limitations in real-world automation.
AI Strengths vs Human Strengths: Where Each Excels
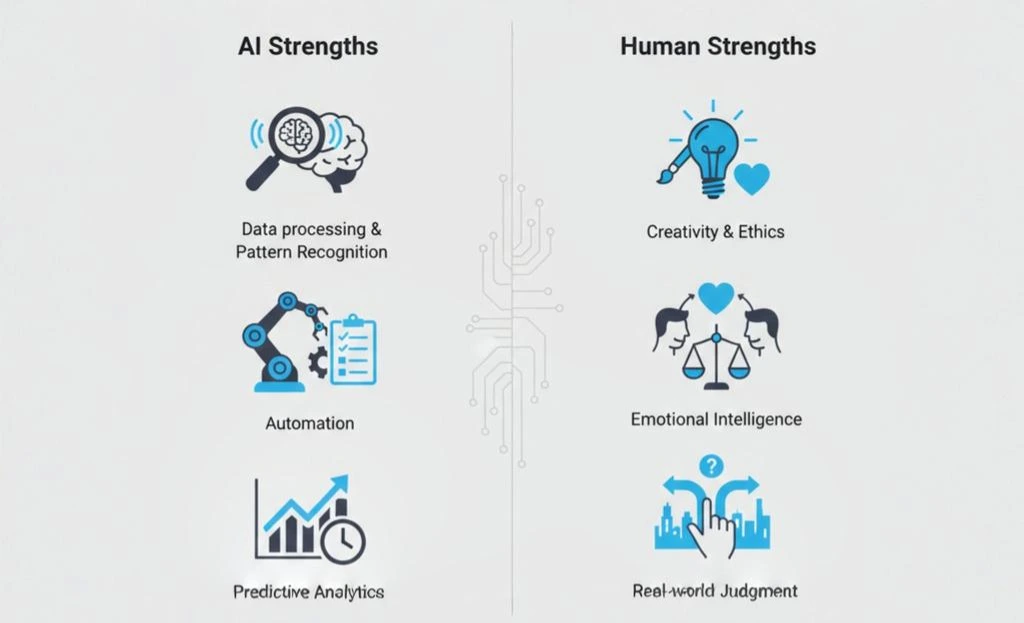
A comparison of artificial intelligence and human intelligence, showing how AI excels in data-driven tasks while humans lead in creativity, emotional intelligence, ethics, and real-world judgment.
Artificial intelligence excels in data-driven tasks such as pattern recognition, large-scale analysis, and automation. Humans, however, lead in creativity, emotional intelligence, ethics, and real-world judgment.
Understanding this balance helps organizations deploy AI where it adds value – without overestimating its capabilities.
4. Creativity, Innovation, and Original Thought
AI is often described as creative, but its creativity is fundamentally different from human creativity.
AI can:
- Generate designs based on existing patterns
- Assist in music, art, and content creation
- Suggest optimizations using historical data
However, it cannot:
- Create ideas without prior data
- Think intuitively or imaginatively
- Understand cultural or emotional significance
Human creativity often emerges from experimentation, curiosity, failure, and hands-on experience. In fields like embedded system design, product development, and research, innovation is driven by real-world problem-solving, something AI cannot truly experience.

5. Ethical Judgment and Moral Responsibility
Ethical decision-making requires an understanding of values, consequences, and long-term impact. AI systems do not possess a moral compass; they simply follow rules and objectives defined by humans.
Key ethical concerns include:
- Algorithmic bias
- Data privacy risks
- Lack of accountability
- Misuse of autonomous technologies
AI cannot be held morally responsible for its actions. Responsibility always lies with:
- Engineers
- Developers
- Organizations
This is particularly critical in safety-sensitive domains such as automotive systems, medical devices, and defense technologies, where ethical judgment and regulatory awareness are essential.
6. Physical Dexterity and Sensorimotor Intelligence
Despite advances in robotics, AI-driven machines still struggle with fine motor skills and adaptive physical interaction.
Human hands can:
- Apply precise and variable pressure
- Adjust movements instantly
- Respond naturally to tactile feedback
Robots rely on:
- Sensors
- Predefined motion models
- Highly controlled environment
In manufacturing, healthcare, and embedded hardware testing, human dexterity and experience remain unmatched.
Can AI Overcome These Limitations?
AI research continues to advance rapidly, improving areas such as:
- Context awareness
- Multimodal reasoning
- Human–AI collaboration
However, many Artificial Intelligence limitations are not merely technical, they are fundamental. Consciousness, empathy, ethics, and lived experience cannot be solved with more data or faster processors.
Rather than replacing humans, AI is best viewed as a powerful tool that enhances human capabilities.
The Role of Human Expertise in an AI-Driven World
In technical fields such as embedded systems, electronics, and industrial automation, AI plays a valuable supporting role. It helps engineers:
- Analyze large datasets
- Speed up development
- Improve efficiency
But it cannot replace:
- Hands-on engineering experience
- System-level thinking
- Real-world problem-solving
Institutions like IIES play a critical role in preparing professionals who understand both advanced technologies and their limitations. Practical training, real hardware exposure, and industry-focused learning remain essential, even in an AI-driven future.

Conclusion: AI Has Limits and That’s a Good Thing
Artificial intelligence has transformed how we work, learn, and innovate. Yet, recognizing Artificial Intelligence limitations reminds us that technology is most powerful when it works with humans, not when it attempts to replace them. True understanding, emotional intelligence, common sense reasoning, creativity, ethical judgment, and physical dexterity remain uniquely human strengths. Acknowledging these boundaries allows us to adopt AI responsibly and use it where it truly adds value. The future does not belong to AI alone, it belongs to people who know how to work with AI, guided by experience, ethics, and expertise.






