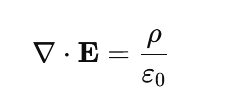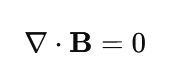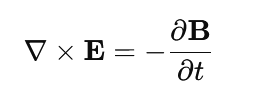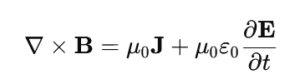What Is Electromagnetic Theory?
Electromagnetic theory involves the examination of electric fields and magnetic fields, as well as their interactions that generate electromagnetic waves. It’s a foundational topic in physics and electrical engineering, and it explains everything from how light works to how your smartphone connects to the internet.
Maxwell’s Equations: The Pillars of Electromagnetic Theory
James Clerk Maxwell unified electricity and magnetism in the 19th century. His four equations are:
1.Gauss’s Law for Electricity
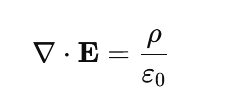
This describes how electric charges produce electric fields.
2.Gauss’s Law for Magnetism
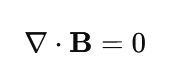
There are no magnetic monopoles—magnetic field lines always form closed loops.
3.Faraday’s Law of Induction
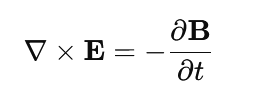
A changing magnetic field induces an electric field (this is how electric generators work).
4.Ampère-Maxwell Law
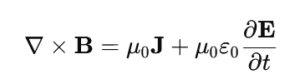
A current or a changing electric field produces a magnetic field.
Key Concepts in Electromagnetic Theory
1.Electric Fields (E-fields)
- Created by electric charges.
- Influence the motion of other charges.
2.Magnetic Fields (B-fields)
- Created by moving charges (currents).
- Affect the direction of moving charges via the Lorentz force.
3.Electromagnetic Waves
- When electric and magnetic fields oscillate together, they form EM waves(like light, radio, X-rays).
- These waves can travel through vacuum at the speed of light c≈3× 10^8 m/s.
4.Wave Propagation
- EM waves propagate through space carrying energy and information.
- The direction of the electric field, magnetic field, and wave propagation are all perpendicular to each other.
Real-World Applications
Electromagnetic theory isn’t just abstract science—it powers the modern world:
Application | How It Works |
Wireless Communication | Uses radio waves (a type of EM wave) to transmit data wirelessly. |
Electric Motors | Magnetic fields convert electrical energy into mechanical motion. |
Optics & Lasers | Light is an electromagnetic wave; its behavior is governed by EM theory. |
Medical Imaging (MRI) | Uses magnetic fields and radio waves to scan the human body. |
Power Transmission | High-voltage AC power lines rely on principles of EM field propagation. |
Why Should You Learn Electromagnetic Theory?
Whether you’re an aspiring engineer, physicist, or tech enthusiast, electromagnetic theory is essential for understanding:
- Antenna design
- High-speed digital circuits
- Fiber optics and photonics
- Wireless sensor networks
- Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC)
It’s not just theory—it’s a toolkit for innovation in modern technology.
Final Thoughts
Electromagnetic theory is a powerful framework that describes a huge range of physical phenomena. Though the fields are invisible, their effects are all around us—from lighting up a room to enabling global communication. By mastering this topic, you’re unlocking the secrets of one of nature’s most fundamental forces.The Indian Institute of Embedded Systems (IIES) is a renowned institution that offers top-notch education and training in the field of embedded systems. With its comprehensive curriculum and experienced faculty, IIES is a leading choice for individuals aspiring to excel in this domain.