Operators
- In programming operators is symbols or special characters
- Performs operations on values and variables
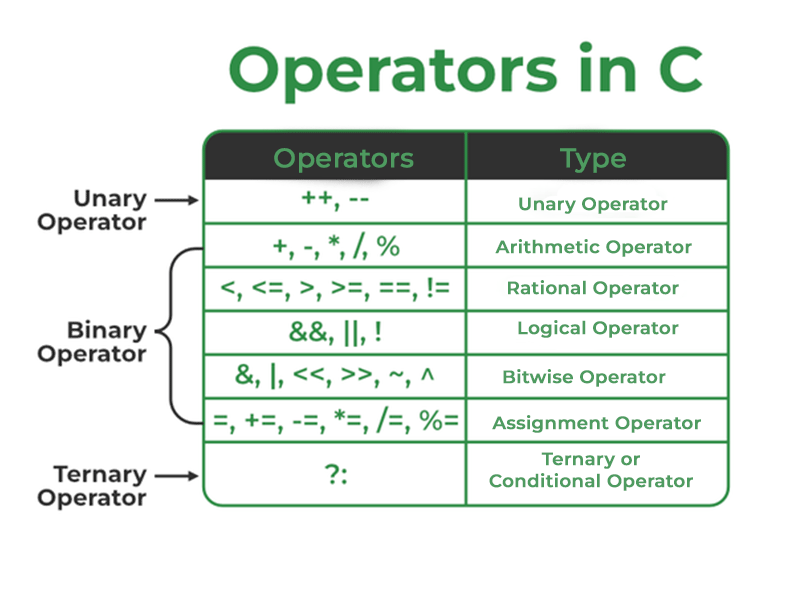
Types of operators in c:
- Arithmetic Operators
- Relational Operators
- Logical Operators
- Bitwise Operators
- Assignment Operators
- Other Operators
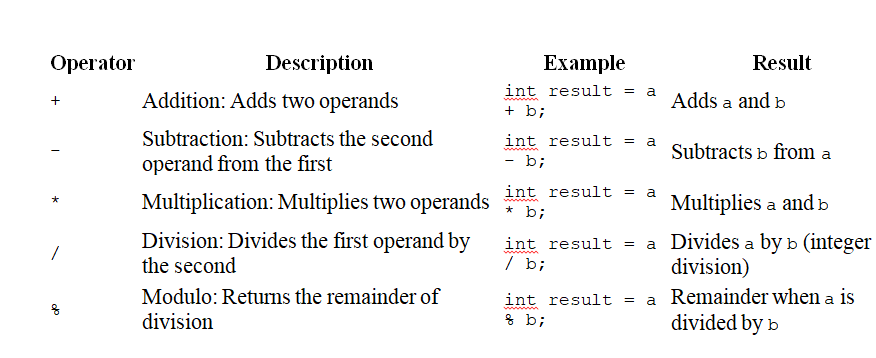
1. Arithmetic Operators:
Simple program on Arithmetic operators:
#include
int main()
{
int a=10;
int b=3;
printf(“%d + %d ==>%d\n”,a,b,a+b);
printf(“%d -%d ==>%d\n”,a,b,a-b);
printf(“%d * %d ==>%d\n”,a,b,a*b);
printf(“%d / %d ==>%d\n”,a,b,a/b);
printf(“%d %% %d ==>%d\n”,a,b,a%b);
return 0;
}
Output :
a+b=10
a-b=7
a*b=30
a/b=3
a%b=1
2. Relational operators:
In C, relational operators are used to compare two values or expressions.
The result is typically represented as 1 for true and 0 for false.
Here’s a table that summarizes the relational operators in C:
Example Program:
#include
int main()
{
int a=10, b=3;
printf(“%d ==%d==>%d\n”,a,b,a==b);
printf(“%d !=%d==>%d\n”,a,b,a!=b);
printf(“%d <=%d==>%d\n”,a,b,a<=b);
printf(“%d >=%d==>%d\n”,a,b,a>=b);
printf(“%d <%d==>%d\n”,a,b,a<b);
printf(“%d >%d==>%d\n”,a,b,a>b);
return 0;
}
#10 ==3==>0
10 !=3==>1
10 <=3==>0
10 >=3==>1
10 <3==>0
10 >3==>1

3. Logical Operators:
- Examples:
- && (Logical AND):
- || (Logical OR): Returns true if at least one condition is true.
- ! (Logical NOT): Reverses the boolean value.
#include
int main()
{
int a=10, b=10;
printf(“%d &&%d==>%d\n”,a<b,a>b,a<b&&a>b);
printf(“%d ||%d==>%d\n”,a<b,a>=b,a=b);
printf(“%d ! %d==>%d\n” ,a,b, a!=b);
return 0;
}

4. Bitwise Operators
Bitwise operators work at the bit level
perform operations directly on the binary representation of integers.
- Examples:
- & (Bitwise AND): Performs AND operation on each bit.
- | (Bitwise OR): Performs OR operation on each bit.
- ^ (Bitwise XOR): Performs XOR operation on each bit.
- ~ (Bitwise NOT): Inverts each bit.
- << (Left Shift): Shifts bits to the left.
- >> (Right Shift): Shifts bits to the right.
int x = 5; // Binary: 0101
int y = 3; // Binary: 0011
printf(“x & y = %d\n”, x & y); // Output: 1 (Binary: 0001)
printf(“x | y = %d\n”, x | y); // Output: 7 (Binary: 0111)
printf(“x ^ y = %d\n”, x ^ y);
printf(“~x = %d\n”, ~x); // Output: -6 (Binary: Inverted 0101)
printf(“x << 1 = %d\n”, x << 1); // Output: 10 (Binary: 1010)
printf(“x >> 1 = %d\n”, x >> 1); // Output: 2 (Binary: 0010)

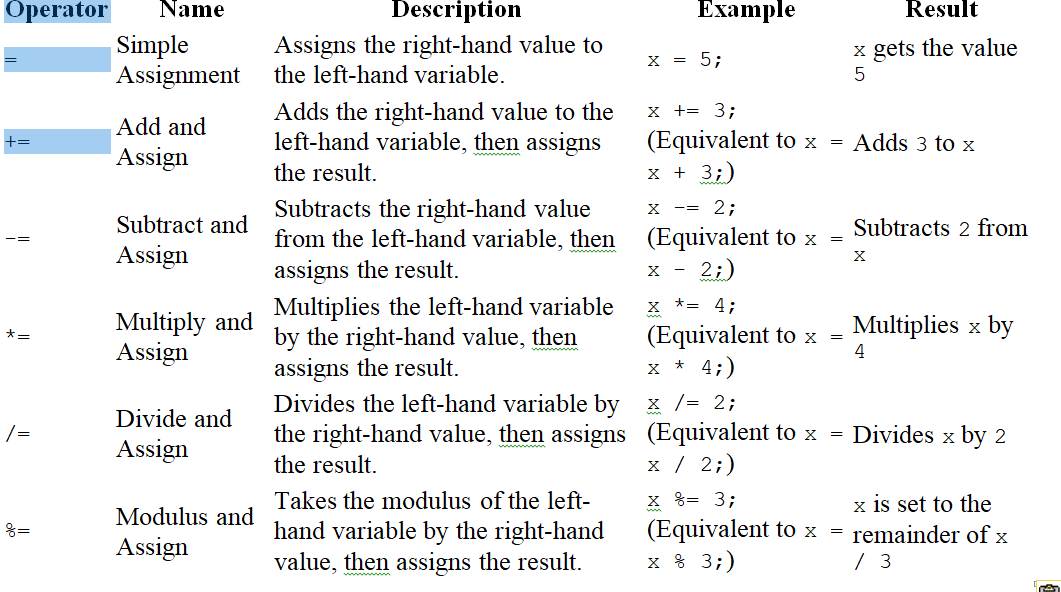
5. Assignment Operators
Assigning the value to variable.
- Examples:
- = (Simple Assignment): Assigns a value.
- += (Add and Assign): Adds a value and assigns the result.
- -= (Subtract and Assign): Subtracts a value and assigns the result.
- *= (Multiply and Assign): Multiplies a value and assigns the result.
- /= (Divide and Assign): Divides a value and assigns the result.
- %= (Modulus and Assign): Computes modulus and assigns the result.
int a = 10;
a += 104; // Same as a = a + 104; ->114;
a -= 104; // Same as a = a – 104; -> a = -94;
a *= 2; // Same as a = a * 2; -> a = 24
a /= 4; // Same as a = a / 4; -> a = 6
a %= 3; // Same as a = a % 3; -> a = 0
printf(” %d\n”, a);
}
6. Other Operators
This category includes miscellaneous operators like the conditional (ternary), sizeof, comma, and type casting operators.
- Examples:
- Conditional Operator (?:): Returns a value based on a condition.
- Comma Operator (,): Evaluates two expressions and returns the result of the second.
- Type Casting Operator: Converts one data type to another.
int x = 10, y = 20;
int max = (x > y) ? x : y;
printf(“Max value = %d\n”, max); // Output: 20
printf(“Size of int = %zu bytes\n”, sizeof(int)); // Output: 4 (typically)
int a = (x > y, y + 5);
printf(“Value of a = %d\n”, a);
float z = (float)x / 3; // Type Casting: Converts x to float for division.
printf(“Value of z = %.2f\n”, z); // Output: 3.33







