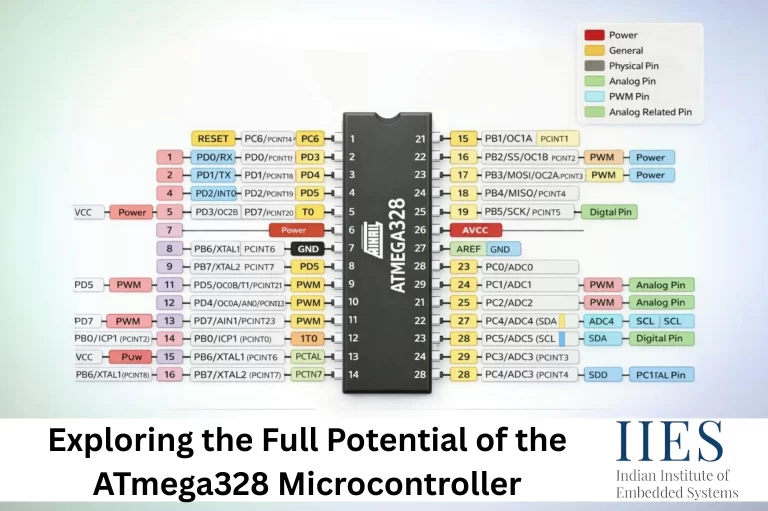
A Brief Background: Why the ATmega328 Still Matters
Originally developed by Atmel (now part of Microchip Technology), the ATmega328 belongs to the AVR (Advanced Virtual RISC) family of microcontrollers. It gained worldwide popularity primarily because it powers one of the most widely used development boards ever created, the Arduino Uno.
What makes the ATmega328 special is not just its specifications, but its balance:
- Enough performance for real-world tasks
- Extremely low power consumption
- Simple architecture that’s easy to understand
- Massive ecosystem and long-term industry support
In an era dominated by ARM-based controllers, the ATmega328 still proves that well-designed 8-bit microcontrollers are far from obsolete.

Core Architecture and Performance Overview
The ATmega328 is an 8-bit microcontroller based on a modified Harvard architecture, meaning it uses separate memory spaces for program code and data. This design improves execution efficiency and allows faster instruction processing.
Key Architectural Highlights:
- Clock Speed: Up to 20 MHz
- Instruction Set: Reduced Instruction Set Computing (RISC)
- Execution Speed: Most instructions execute in a single clock cycle
- Package Options: DIP, TQFP, QFN
This architecture allows the ATmega328 to deliver predictable, real-time performance, an essential requirement for embedded and control-based applications.
Memory Configuration: Designed for Practical Applications
Memory plays a critical role in determining what a microcontroller can realistically handle. The ATmega328 offers a well-balanced memory layout that suits both beginner and intermediate-level projects.
1. Flash Memory (32 KB)
The microcontroller includes 32 KB of in-system programmable flash memory, used to store application code. This is more than sufficient for:
- Sensor processing algorithms
- Control logic
- Communication stacks
- Bootloaders
Thanks to efficient AVR instruction encoding, developers can implement surprisingly complex logic within this space.
2. SRAM (2 KB)
The 2 KB of SRAM is used for runtime variables, buffers, and stack operations. While this may seem limited by modern standards, careful memory management allows smooth execution of:
- Sensor data handling
- Communication buffers
- Real-time control tasks
This limitation also teaches developers good programming discipline, which is invaluable in embedded design.
3. EEPROM (1 KB)
The 1 KB of EEPROM provides non-volatile storage, making it ideal for:
- Configuration parameters
- Calibration data
- User settings
Even when power is lost, EEPROM data remains intact, an essential feature for embedded products.
Rich Peripheral Set: Small Chip, Big Capabilities
One of the strongest reasons for the ATmega328’s long-term success is its built-in peripheral support.
Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC)
- 10-bit resolution
- Up to 8 analog input channels
- Ideal for reading sensors like temperature, pressure, light, and voltage
Timers and Counters
- Three timers (8-bit and 16-bit)
- Support for input capture, output compare, and precise timing
These timers are critical for applications such as:
- Motor control
- Frequency measurement
- Time-based task scheduling
PWM (Pulse Width Modulation)
- Multiple PWM channels
Used for:
- Motor speed control
- LED brightness control
- Power regulation
Communication Interfaces: Enabling Connectivity
Modern embedded systems rarely work in isolation. The ATmega328 supports multiple communication protocols that make it easy to integrate with other devices.
Supported Interfaces:
- USART: Serial communication for debugging and data exchange
- SPI: High-speed communication with displays, memory, and sensors
- I2C (TWI): Multi-device communication over just two wires
These interfaces allow the ATmega328 to act as:
- A controller
- A data acquisition node
- A communication bridge

Power Efficiency: Ideal for Battery-Powered Designs
Low power consumption is one of the ATmega328’s strongest advantages.
Power-Saving Features:
- Multiple sleep modes (Idle, Power-down, Standby)
- Peripheral-level power control
- Low-voltage operation
This makes it well-suited for:
- Wearable electronics
- Wireless sensor nodes
- Portable measurement devices
With proper power management, ATmega328-based systems can run for months, or even years, on small batteries.
Arduino Ecosystem: A Game Changer
The ATmega328 became a household name largely because of Arduino. The Arduino Uno board made embedded development accessible to millions by simplifying both hardware and software.
Why Arduino + ATmega328 Works So Well:
- Beginner-friendly development environment
- Massive library support
- Strong global community
- Rapid prototyping capabilities
While professionals may later transition to bare-metal AVR programming or other architectures, Arduino often serves as the first gateway into embedded systems.
Real-World Applications of the ATmega328
Despite being an 8-bit controller, the ATmega328 is actively used across many domains.
1. Home Automation
- Smart lighting control
- Sensor-based automation
- Energy monitoring
Its low power consumption and communication support make it ideal for distributed smart home nodes.
2. Robotics
- Motor control
- Sensor fusion
- Basic decision-making
Many educational and hobby robotics platforms rely on the ATmega328 due to its predictable timing and PWM capabilities.
3. Data Logging Systems
- Environmental monitoring
- Industrial parameter tracking
- Portable measurement tools
EEPROM and flash memory make long-term data storage feasible.
4. Education and Skill Development
The ATmega328 is widely used in:
- Engineering colleges
- Technical training institutes
- Embedded systems courses
It helps learners understand core concepts like registers, interrupts, timers, and communication protocols.
5. Wearable and Portable Devices
Thanks to its small footprint and efficiency, it fits well in:
- Fitness trackers
- Custom health monitors
- Compact consumer electronics
Is the ATmega328 Still Relevant Today?
Absolutely, when used for the right applications.
While it may not replace high-performance ARM processors in complex IoT gateways or AI-driven devices, the ATmega328 remains a strong choice for:
- Control-oriented systems
- Low-power designs
- Cost-sensitive products
- Learning and prototyping
Its long production life, extensive documentation, and industry adoption make it a safe and dependable option.

Conclusion
The ATmega328 microcontroller has stood the test of time not because it is the most powerful, but because it is practical, reliable, and efficient. It strikes a rare balance between simplicity and capability, making it suitable for beginners and experienced developers alike. In a fast-changing technology landscape, components that offer clarity, predictability, and long-term support remain invaluable. Whether you are building your first embedded project, teaching electronics, or designing a focused real-world application, the ATmega328 continues to prove that good engineering never goes out of style.