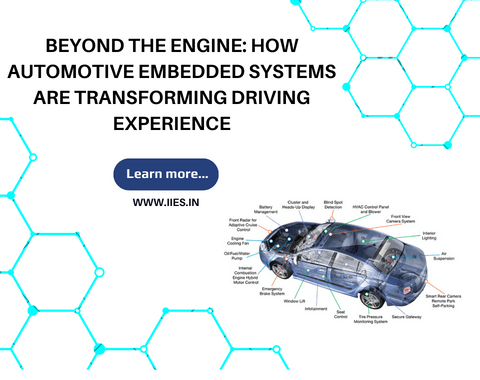
The role of embedded systems in the automotive domain is significant as it is primarily responsible for transforming the vehicle’s performance, safety, functionality, and comfort. Embedded systems do this by integrating various devices and sensors that are designed to work together to provide optimal performance and efficiency. For instance, embedded systems are used to control the engine, which is the heart of every vehicle. By modifying the engine’s fuel injection and ignition timing, embedded systems can optimize the engine’s performance, reduce emissions, and increase fuel efficiency.
Embedded systems are also important in vehicle safety. They are used to control various safety features such as airbags, traction control, stability control, and anti-lock braking systems. By monitoring the vehicle’s speed, torque, and position in real time, embedded systems can make quick and accurate adjustments to the vehicle’s operation to prevent the occurrence of accidents.
Moreover, embedded systems are used in infotainment systems, which provide entertainment and information to the driver and passengers. These systems are designed to offer a range of multimedia features such as audio, video, and navigation systems.