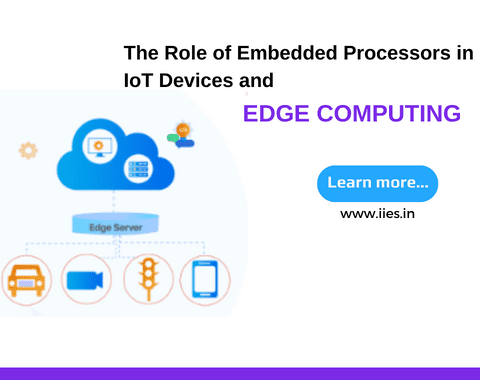
An edge computing system consists of three main components: edge devices, edge devices’ local infrastructure, and the cloud.
Firstly, the edge devices, such as IoT sensors, actuators, and embedded systems, collect data from the physical world. These devices are equipped with embedded processors that process, analyze, and filter data in real time. The embedded processors play a critical role in executing algorithms, running AI models, and making decisions based on the data received.
Next, the edge devices’ local infrastructure comprises gateways, edge servers, and network resources. These components provide the necessary connectivity, storage, and computing power required for edge processing. The embedded processors within the edge devices work in conjunction with the local infrastructure to enable efficient data processing and analysis.
Lastly, the cloud acts as a central hub for aggregating, storing, and analyzing data from multiple edge devices. While cloud computing is crucial for certain tasks, such as long-term storage, complex data analytics, and training machine learning models, edge computing ensures that critical time-sensitive operations are performed closer to the data source, reducing latency and improving overall system performance.