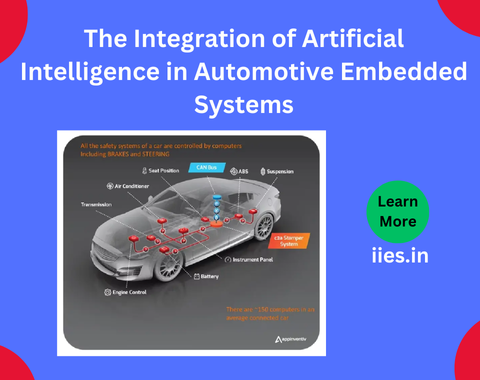
AI, particularly machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL), allows embedded systems to evolve from mere executors of code to intelligent systems capable of learning from data and adapting to new situations. By integrating AI into automotive embedded systems, vehicles can now make real-time decisions, improve safety, and provide an enhanced driving experience.
Some of the core areas where AI is making a significant impact include:
1. Autonomous Driving and Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS)
One of the most prominent applications of AI in automotive embedded systems is autonomous driving. AI algorithms process data from various sensors, including cameras, radar, LIDAR, and ultrasonic sensors, to enable a vehicle to perceive its surroundings. Using this data, AI models can identify objects, interpret traffic signals, monitor lane markings, and make split-second decisions that ensure the vehicle’s safety and efficiency.
For instance, Tesla’s Autopilot and other ADAS systems use AI to enhance features like lane-keeping, adaptive cruise control, and automated parking. These AI-powered embedded systems continually learn from driving conditions and user inputs to improve their performance over time, creating a seamless integration of autonomous functionality in regular driving scenarios.
2. Predictive Maintenance
AI also plays a critical role in predictive maintenance, a feature that significantly reduces vehicle downtime and operational costs. Traditional embedded systems in vehicles monitor engine performance, fuel efficiency, and various other parameters, but they lack the ability to predict future issues.
With AI, embedded systems can now analyze historical data from sensors and predict when components such as brakes, tires, or batteries are likely to fail. This proactive approach enables early detection of potential issues, minimizing the risk of unexpected breakdowns and enhancing vehicle longevity. Predictive maintenance is particularly beneficial in fleet management, where keeping multiple vehicles in optimal condition is crucial for operational efficiency.
3. In-Vehicle Infotainment and Personalization
AI is transforming in-vehicle infotainment systems by creating personalized experiences for drivers and passengers. By analyzing data such as user preferences, driving habits, and even biometric information, AI-powered embedded systems can suggest personalized music playlists, adjust the seat and climate settings, and provide real-time route recommendations based on traffic and weather conditions.
Voice assistants like Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, and Apple’s Siri are increasingly being integrated into vehicles, providing a hands-free interface for drivers. These AI-driven systems allow users to control various functions, such as navigation, calling, and media playback, with natural language processing (NLP) and speech recognition, enhancing safety by reducing distractions.
4. Enhanced Safety Systems
Safety is paramount in the automotive industry, and AI’s role in improving vehicle safety cannot be overstated. Embedded AI systems help vehicles detect potential hazards, including pedestrians, cyclists, and other vehicles, and respond accordingly to avoid accidents.
For example, AI is behind features like automatic emergency braking, collision avoidance, and pedestrian detection. These systems rely on machine learning models to process data from sensors in real time, accurately assess the driving environment, and make decisions faster than a human driver could. AI’s continuous learning capability also enables these systems to adapt to new safety scenarios, making them more robust over time.
5. Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) Communication
AI is enhancing the capabilities of Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) communication, which allows vehicles to exchange data with other vehicles (V2V), infrastructure (V2I), and even pedestrians (V2P). This interconnected network of vehicles and infrastructure enhances traffic flow, reduces congestion, and improves overall road safety.
AI processes the vast amounts of data transmitted via V2X systems, making sense of complex interactions in real-time. For example, AI can predict traffic patterns, reroute vehicles to avoid congestion, and even assist in coordinating autonomous vehicles to drive in formation for fuel efficiency.
Challenges in Integrating AI into Automotive Embedded Systems
While the integration of AI in automotive embedded systems is unlocking immense potential, it also presents several challenges:
1. Processing Power and Latency
AI algorithms, especially those involving deep learning, require significant computational resources. Traditional embedded systems often lack the processing power to handle these AI workloads. To address this, manufacturers are increasingly turning to high-performance processors, such as GPUs and specialized AI chips like NVIDIA’s Xavier and Tesla’s Dojo, to meet the demands of AI-driven functions.
2. Data Privacy and Security
With AI-driven vehicles collecting vast amounts of data, privacy and security concerns are becoming more prominent. Ensuring that sensitive data, such as location and biometric information, is stored and transmitted securely is critical. Moreover, AI systems in vehicles must be safeguarded against cyberattacks, which could lead to catastrophic consequences if a vehicle’s control systems are compromised.
3. Safety and Regulatory Compliance
As AI takes on a more prominent role in vehicle operations, ensuring compliance with automotive safety standards like ISO 26262 and the SOTIF (Safety of the Intended Functionality) standard becomes crucial. AI models must be thoroughly tested and validated to ensure they behave predictably and reliably under all conditions.
4. Cost and Complexity
The integration of AI into embedded systems significantly increases the complexity of vehicle design and production. AI development requires highly specialized knowledge, and implementing AI into automotive systems can be cost-prohibitive for some manufacturers, particularly smaller companies.
The Road Ahead: The Future of AI in Automotive Embedded Systems
Despite the challenges, the future of AI in automotive embedded systems looks incredibly promising. As AI technology continues to evolve, we can expect more sophisticated autonomous driving systems, enhanced safety features, and increasingly personalized in-car experiences. The integration of AI will also drive innovations in electric and connected vehicles, leading to more sustainable and efficient transportation systems.
AI’s ability to learn and adapt will result in cars that improve over time, offering safer, more efficient, and more enjoyable driving experiences. With advancements in processing power, better algorithms, and a growing focus on security, AI-powered embedded systems will continue to push the boundaries of what’s possible in the automotive industry.
Conclusion
The integration of AI in automotive embedded systems is revolutionizing how vehicles operate, communicate, and interact with their environment. From autonomous driving to predictive maintenance, AI is empowering vehicles to become smarter, safer, and more efficient. While challenges remain, the transformative potential of AI in the automotive sector is undeniable, and as technology advances, we are poised to witness a new era of intelligent, AI-driven vehicles shaping the future of transportation.