What is CAN Protocol?
Controller Area Network (CAN) is a serial communication protocol widely used for reliable data exchange between Electronic Control Units (ECUs)—especially in automotive systems. One of its main advantages is that it allows communication without requiring a host computer. Unlike traditional address-based protocols, CAN is a message-based protocol.
Why Use CAN Protocol?
Originally developed for automotive applications, CAN’s primary use is for in-vehicle electronic networking. It was designed to replace complex and bulky wiring harnesses with a simple two-wire bus system.
Developed by Robert Bosch GmbH in 1983 to enhance automobile safety, reliability, and fuel efficiency.
Though initially aimed at automotive networks, CAN is now widely adopted in industrial, medical, and aerospace sectors.
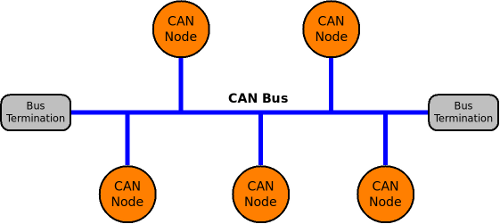
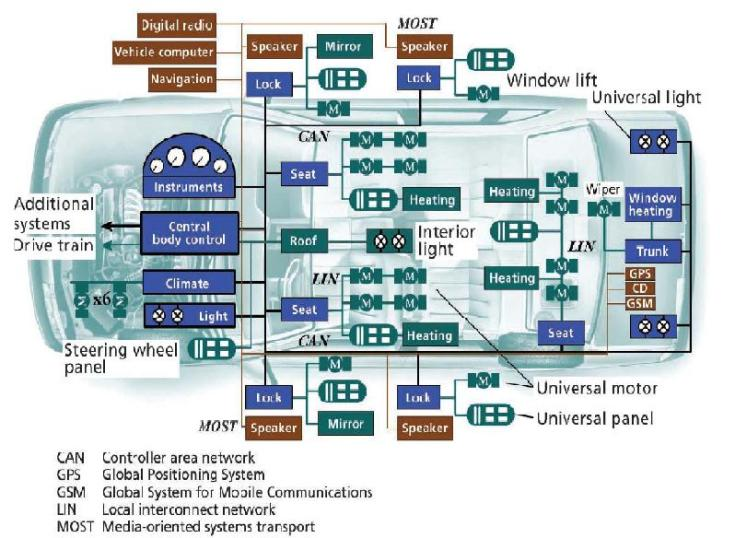
On-Board Diagnostics (OBD)
CAN is one of the five protocols used in the OBD (On-Board Diagnostics) standard for vehicle diagnostics. This makes it an essential part of modern automotive design for troubleshooting and monitoring performance.
Key Features of the CAN Bus
Invented by Bosch in 1986.
Uses two wires:
CANH (CAN High)
CANL (CAN Low)
Characteristics of CAN Protocol:
Speed & Distance:
Up to 1 Mbps for networks shorter than 40 meters
Lower speeds allow longer distances
Example: 125 Kbps can reach up to 500 meters
Maximum Nodes:
CAN Versions:
Layered Architecture (for flexibility and transparency):
Supported Topologies:
Advantages:
Data Transmission:
Supports:
Error Detection:
Bit error
Acknowledgment error
Form error
CRC error
Stuff error
Message Priority Handling:
Data Format:
Applications of CAN Protocol
Passenger cars, buses, trucks (gasoline and electric)
Aviation and navigation systems
Industrial automation and process control
Elevators and escalators
Building automation systems
Medical equipment and instruments
Conclusion
Understanding the CAN protocol is more than just technical knowledge—it’s a gateway to creating smarter, more efficient embedded systems. As industries move toward greater automation and connectivity, the ability to design and manage real-time communication networks using CAN is becoming a vital skill.
At the Indian Institute of Embedded Systems (IIES), students go beyond theory to explore how CAN works in actual automotive and industrial applications. With hands-on experience, personalized mentorship, and job-oriented training, learners build the confidence to design systems that are reliable, scalable, and industry-ready.
Whether you’re working on vehicle electronics, building smart machines, or exploring embedded systems development, IIES gives you the practical foundation and technical edge needed to thrive in this field.
Step into the future of embedded communication with IIES—where you don’t just learn protocols, you build the systems that run on them.



