1. End Devices (Nodes): These are the sensors or devices that collect data and transmit it to the network. End devices can be anything from temperature sensors and GPS trackers to smart meters and industrial sensors.
2. Gateways: Gateways act as bridges between the end devices and the network server. Gateways are essential for covering a large geographic area and ensuring connectivity.
3. Network Server: The network server manages the communication between end devices and applications. It handles tasks such as device authentication, encryption, and data rate management.
4. Application Server: This server processes the data received from end devices and translates it into a format that can be easily utilized by the end-user application.
Advantages of LoRaWAN Technology:
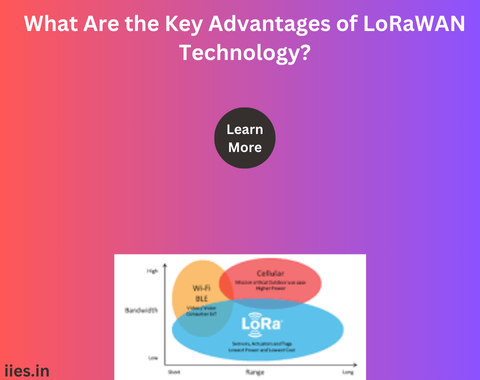
1. Long Range: One of the defining features of LoRaWAN is its exceptional range. It can cover distances of several kilometers in urban environments and even greater distances in rural areas. This makes it ideal for applications that require connectivity over large geographic areas.
2. Low Power Consumption: LoRaWAN devices are designed to operate on minimal power, making them suitable for battery-operated devices. The low power consumption ensures that devices can operate for extended periods without the need for frequent battery replacements.
3. Scalability: LoRaWAN networks are highly scalable, allowing for the connection of a vast number of devices. This scalability makes it adaptable to a wide range of applications, from smart cities and agriculture to industrial IoT.
4. Cost-Effective: The infrastructure required for deploying LoRaWAN networks is cost-effective compared to some other IoT connectivity options. The low-power requirements of devices also contribute to the overall cost efficiency of LoRaWAN technology.
Applications of LoRaWAN Technology:
1. Smart Cities: LoRaWAN enables the deployment of smart city solutions, such as intelligent street lighting, waste management systems, and environmental monitoring. The long-range capability is particularly advantageous for covering large urban areas.
2. Agriculture: In agriculture, LoRaWAN is used for precision farming applications. It facilitates the monitoring of soil conditions, crop health, and weather parameters. Farmers can make data-driven decisions to optimize crop yields and resource usage.
3. Industrial IoT (IIoT): LoRaWAN is well-suited for industrial applications where sensors and devices need to communicate over long distances. It is employed in predictive maintenance, asset tracking, and monitoring of equipment and facilities.
4. Smart Buildings: Building automation systems leverage LoRaWAN for energy management, security, and occupancy monitoring. The long-range capability ensures that devices throughout a building can stay connected to the network.
5. Logistics and Supply Chain: LoRaWAN is used in logistics and supply chain management for real-time tracking of goods. It provides accurate location data and helps optimize the movement of products throughout the supply chain.
Impact on IoT Landscape:
LoRaWAN technology is reshaping the IoT landscape by addressing the limitations of traditional connectivity solutions. Its long-range capability, combined with low power consumption, opens up new possibilities for IoT applications in diverse sectors. As more industries recognize the potential of LoRaWAN, its adoption is expected to grow, leading to a more connected and efficient world