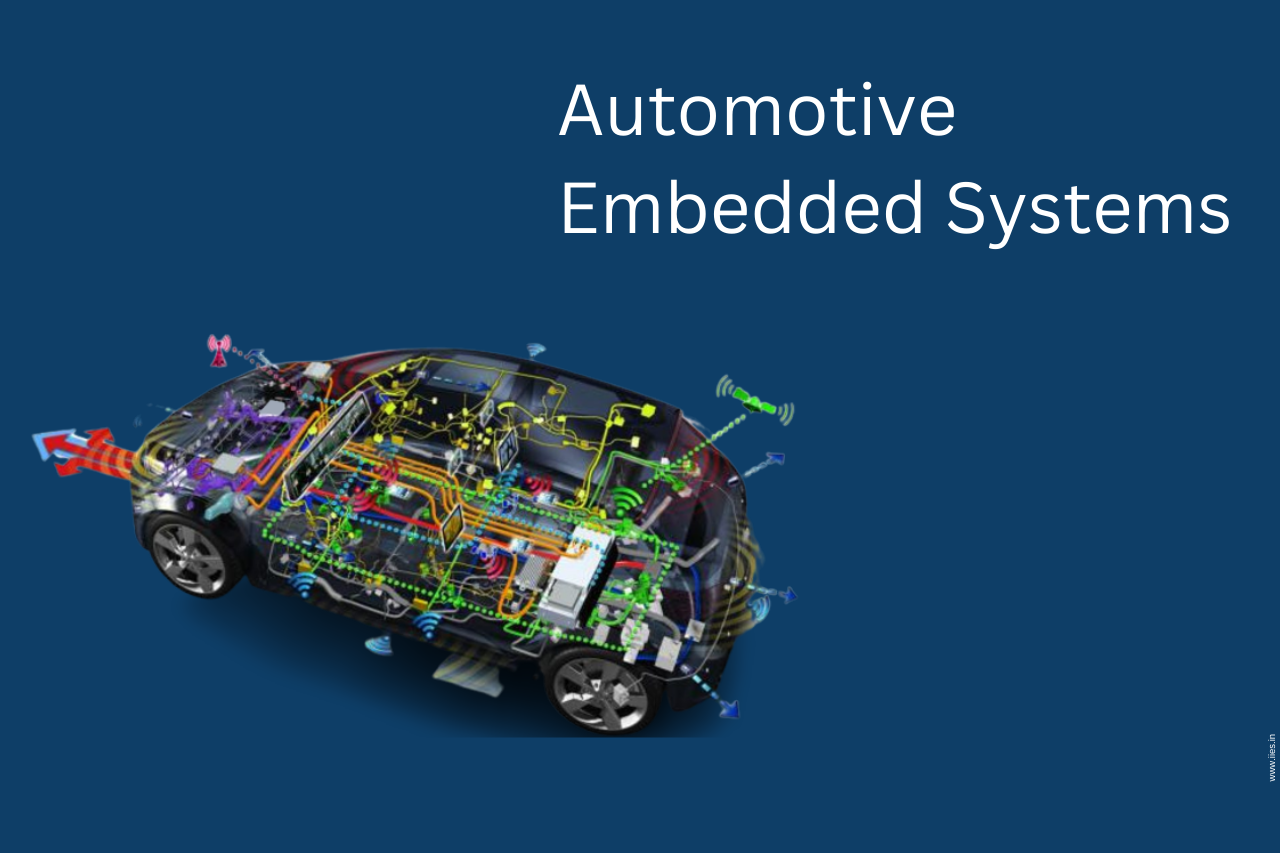
Engine:- The internal combustion engine is the beating heart and soul of your car. The timing chain, camshaft, crankshaft, spark plugs, cylinder heads, valves, and pistons are some of the components found in the engine block.
Transmission:- The gearbox, which is a gearbox full of gears and gear trains, efficiently utilizes the torque of the engine to change ratios and propel the vehicle.
Battery:- The battery provides the electricity required to power the electrical systems in your car. Your automobile won’t run without a battery.
Alternator:- As a component of the electrical system, the alternator powers the electrical system while your automobile is operating and charges the battery.
Radiator:- By eliminating heat from coolant before it is circulated back through the engine, the radiator aids in keeping the engine cool.
Brakes:- Your brakes are one of the most crucial safety features on your car and are located on all four wheels. Both the front and rear wheels have disc brakes, which are equipped with calipers and brake pads. On the back wheels of some cars, you might find drum brakes with brake shoes and wheel cylinders.