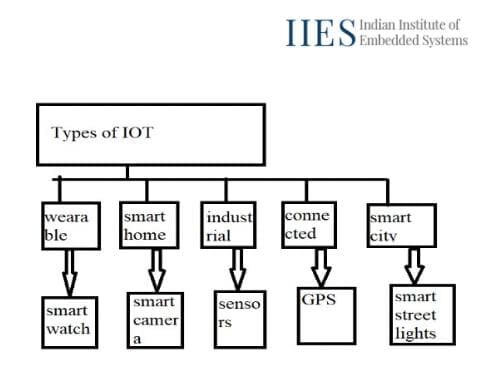
Absolutely! While a technical background can be advantageous when learning IoT, it is not an absolute requirement. IoT encompasses a wide range of skills and knowledge, including electronics, programming, networking, and data analytics. As a non-technical background learner, you can start by gaining a foundational understanding of these concepts through online courses, workshops, or tutorials. With dedication and persistence, you can learn the necessary skills and gradually build your expertise in IoT. Focus on acquiring practical skills, exploring hands-on projects, and collaborating with others in the field. Networking with professionals, attending IoT events, and participating in online communities can also provide valuable insights and guidance. With a strong learning mindset and an eagerness to explore, you can successfully embark on a career in IoT, regardless of your technical background.