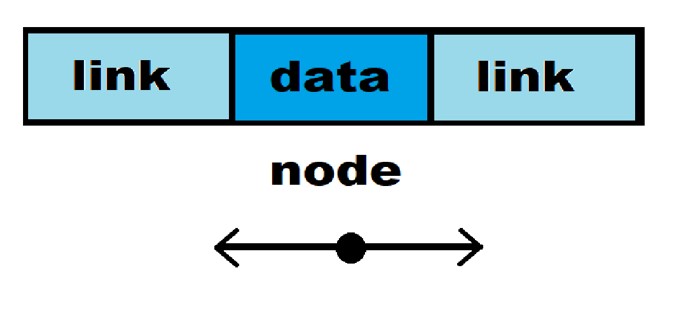
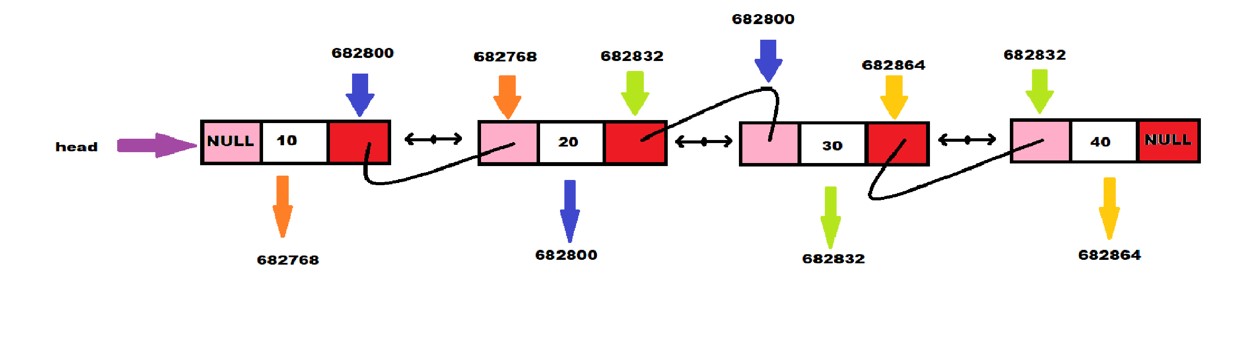
Node Structure Definition
The structure of a node in a doubly linked list is defined as follows:
typedef struct dll {
int data; // Value of the node
struct dll *nlink; // Pointer to the next node
struct dll *plink; // Pointer to the previous node
} node;
Implement a Doubly Linked List in C
To create a doubly linked list that supports the following functionalities:
- Insert a node at the front.
- Insert a node at the end.
- Insert a node at a specific position.
- Delete a node from the front.
- Delete a node from the end.
- Delete a node from a specific position.
- Display all nodes in the list.
- Display all nodes in reverse order.
- Check if the list is a palindrome.
- Reverse the entire list.
- Search for a specific element.
- Sort the list in ascending order.
- Sort the list in descending order.
Code :
#include
#include
typedef struct dll {
int data;
struct dll *nlink;
struct dll *plink;
} node;
node *head = NULL;
node *memalloc(int d) {
node *newNode = (node *)malloc(sizeof(node));
if (newNode == NULL) {
printf(“Memory not allocated\n”);
exit(1);
}
newNode->data = d;
newNode->nlink = NULL;
newNode->plink = NULL;
return newNode;
}
void insertAtFront(int d) {
node *newNode = memalloc(d);
if (head == NULL) {
head = newNode;
return;
}
newNode->nlink = head;
head->plink = newNode;
head = newNode;
}
void insertAtEnd(int d) {
node *newNode = memalloc(d);
if (head == NULL) {
head = newNode;
return;
}
node *temp = head;
while (temp->nlink != NULL) {
temp = temp->nlink;
}
temp->nlink = newNode;
newNode->plink = temp;
}
int countNodes() {
int count = 0;
node *temp = head;
while (temp != NULL) {
temp = temp->nlink;
count++;
}
printf(“The number of list elements is: %d\n”, count);
return count;
}
void insertAtPosition() {
int d, pos, c;
c = countNodes();
if (head == NULL) {
printf(“Your list is empty\n”);
printf(“Enter your first node\n”);
printf(“Enter the data element: “);
scanf(“%d”, &d);
insertAtFront(d);
return;
}
printf(“Enter the position: “);
scanf(“%d”, &pos);
if (pos < 0 || pos > c) {
printf(“Enter a valid position\n”);
return;
}
printf(“Enter the list data: “);
scanf(“%d”, &d);
if (pos == 0) {
insertAtFront(d);
return;
}
if (pos == c) {
insertAtEnd(d);
return;
}
node *newNode = memalloc(d);
node *temp = head;
for (int i = 1; i < pos; i++) {
temp = temp->nlink;
}
newNode->nlink = temp->nlink;
newNode->plink = temp;
if (temp->nlink != NULL) {
temp->nlink->plink = newNode;
}
temp->nlink = newNode;
}
void deleteFromFront() {
if (head == NULL) {
printf(“Your linked list is empty\n”);
exit(1);
}
node *temp = head;
head = temp->nlink;
if (head != NULL) {
head->plink = NULL;
}
free(temp);
}
void deleteFromEnd() {
if (head == NULL) {
printf(“Your linked list is empty\n”);
exit(1);
}
node *temp = head;
while (temp->nlink != NULL) {
temp = temp->nlink;
}
if (temp->plink != NULL) {
temp->plink->nlink = NULL;
} else {
head = NULL; // List becomes empty
}
free(temp);
}
void deleteAtPosition() {
int pos, c;
c = countNodes();
if (head == NULL) {
printf(“Your linked list is empty\n”);
exit(1);
}
printf(“Enter the position: “);
scanf(“%d”, &pos);
if (pos < 0 || pos >= c) {
printf(“Enter a valid position\n”);
return;
}
if (pos == 0) {
deleteFromFront();
return;
}
if (pos == c – 1) {
deleteFromEnd();
return;
}
node *temp = head;
for (int i = 0; i < pos; i++) {
temp = temp->nlink;
}
temp->plink->nlink = temp->nlink;
if (temp->nlink != NULL) {
temp->nlink->plink = temp->plink;
}
free(temp);
}
void display() {
if (head == NULL) {
printf(“Your linked list is empty\n”);
return;
}
node *temp = head;
printf(“The data elements are: “);
while (temp != NULL) {
printf(“%d “, temp->data);
temp = temp->nlink;
}
printf(“\n”);
}
void displayReverse() {
if (head == NULL) {
printf(“Your linked list is empty\n”);
return;
}
node *temp = head;
while (temp->nlink != NULL) {
temp = temp->nlink;
}
printf(“The data elements in reverse are: “);
while (temp != NULL) {
printf(“%d “, temp->data);
temp = temp->plink;
}
printf(“\n”);
}
void checkPalindrome() {
if (head == NULL) {
printf(“Your linked list is empty\n”);
return;
}
node *temp = head;
node *revTemp = NULL;
// Create a reverse copy of the list
while (temp != NULL) {
node *newNode = memalloc(temp->data);
newNode->nlink = revTemp;
if (revTemp != NULL) {
revTemp->plink = newNode;
}
revTemp = newNode;
temp = temp->nlink;
}
// Compare original list and reversed list
temp = head;
node *checkTemp = revTemp;
int isPalindrome = 1;
while (temp != NULL && checkTemp != NULL) {
if (temp->data != checkTemp->data) {
isPalindrome = 0;
break;
}
temp = temp->nlink;
checkTemp = checkTemp->nlink;
}
if (isPalindrome) {
printf(“The given list is a palindrome\n”);
} else {
printf(“The given list is not a palindrome\n”);
}
// Free the reversed list
while (revTemp != NULL) {
node *toFree = revTemp;
revTemp = revTemp->nlink;
free(toFree);
}
}
void reverseList() {
if (head == NULL) {
printf(“Your linked list is empty\n”);
return;
}
node *temp = head;
node *prev = NULL;
while (temp != NULL) {
node *next = temp->nlink;
temp->nlink = prev;
temp->plink = next;
prev = temp;
temp = next;
}
head = prev;
}
void searchElement() {
int key;
printf(“Enter the key element: “);
scanf(“%d”, &key);
node *temp = head;
while (temp != NULL) {
if (key == temp->data) {
printf(“Data Found\n”);
return;
}
temp = temp->nlink;
}
printf(“Data not found\n”);
}
void sortListAscending() {
int swapped;
do {
node *temp = head;
swapped = 0;
while (temp != NULL && temp->nlink != NULL) {
if (temp->data > temp->nlink->data) {
int t = temp->data;
temp->data = temp->nlink->data;
temp->nlink->data = t;
swapped = 1;
}
temp = temp->nlink;
}
} while (swapped);
}
void sortListDescending() {
int swapped;
do {
node *temp = head;
swapped = 0;
while (temp != NULL && temp->nlink != NULL) {
if (temp->data < temp->nlink->data) {
int t = temp->data;
temp->data = temp->nlink->data;
temp->nlink->data = t;
swapped = 1;
}
temp = temp->nlink;
}
} while (swapped);
}
int main() {
int opt, d;
while (1) {
printf(“1. Insert Front\n2. Insert End\n3. Insert Position\n4. Delete Front\n5. Delete End\n”
“6. Display\n7. Display Reverse\n8. Delete Position\n9. Reverse List\n”
“10. Check Palindrome\n11. Sort Ascending\n12. Sort Descending\n13. Exit\n”);
printf(“Enter your option: “);
scanf(“%d”, &opt);
switch (opt) {
case 1:
printf(“Enter the value: “);
scanf(“%d”, &d);
insertAtFront(d);
break;
case 2:
printf(“Enter the value: “);
scanf(“%d”, &d);
insertAtEnd(d);
break;
case 3:
insertAtPosition();
break;
case 4:
deleteFromFront();
break;
case 5:
deleteFromEnd();
break;
case 6:
display();
break;
case 7:
displayReverse();
break;
case 8:
deleteAtPosition();
break;
case 9:
reverseList();
break;
case 10:
checkPalindrome();
break;
case 11:
sortListAscending();
break;
case 12:
sortListDescending();
break;
case 13:
exit(0);
default:
printf(“Invalid option. Please try again.\n”);
}
}
return 0;
}