Common Operations in SLL
- insertfront: inserting a new node at the beginning of the current list.
- insertend: inserting a new node at the end of the current list.
- deletefront: deleting the first node from the current list.
- deleteend: deleting the last node from the current list.
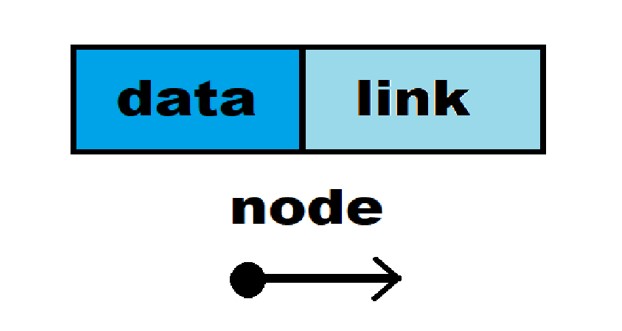
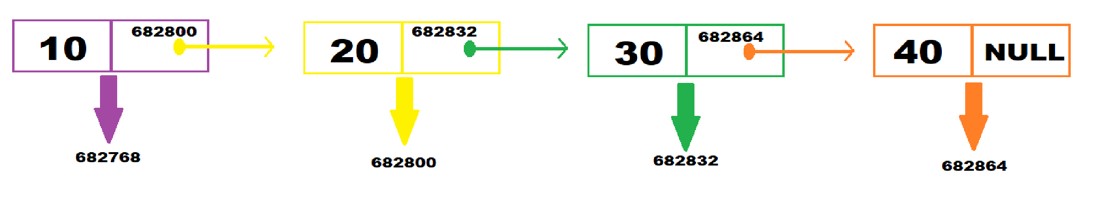
Using Structures in Linked Lists
- Linked lists use self-referential structures to define nodes.
- A self-referential structure is a structure that holds a pointer to another structure of the same type.
Example of a Self-Referential Structure
struct node {
int data;
struct node *link; // Self-referential structure
};
Why Use a Structure?
- Grouping of related data (data and link) into a single entity.
- Dynamic memory allocation: Nodes can be created and removed at runtime, making it easier to manage the linked list’s size.
- Efficient memory usage: Only as much memory as needed is allocated.
Linked List Implementation:
- Implement a C program to create a singly linked list (SLL) and perform the following operations based on the user’s choice:
- Insert at the front
- Insert at the end
- Insert at a specific position
- Delete from the front
- Delete from the end
- Display the list
#include<stdio.h>
typedef struct s1{
int data;
struct s1 *link;
} node;
node *head = NULL;
node *memalloc(int d){
node *new = (node *)malloc(sizeof(node));
if(new == NULL){
printf(“Memory not allocated\n”);
exit(1);
}
new->data = d;
new->link = NULL;
return new;
}
void insertFront(int d){
node *new = memalloc(d);
if(head == NULL){
head = new;
return;
}
new->link = head;
head = new;
}
void insertEnd(int d){
node *new = memalloc(d);
if(head == NULL){
head = new;
return;
}
node *temp = head;
while(temp->link != NULL){
temp = temp->link;
}
temp->link = new;
}
int countList(){
int count = 0;
node *temp = head;
while(temp != NULL){
temp = temp->link;
count++;
}
printf(“The number of elements in the list: %d\n”, count);
return count;
}
void insertAtPosition(){
int pos, d;
int count = countList();
if(count == 0){
printf(“List is empty\n”);
printf(“Adding new node\n”);
printf(“Enter the value: “);
scanf(“%d”, &d);
insertFront(d);
return;
}
printf(“Enter the position between 0 – %d: “, count);
scanf(“%d”, &pos);
if(pos < 0 || pos > count){
printf(“Invalid position. Position out of bounds.\n”);
return;
}
printf(“Enter the value: “);
scanf(“%d”, &d);
if(pos == 0){
insertFront(d);
return;
}
if(pos == count){
insertEnd(d);
return;
}
node *new = memalloc(d);
node *temp = head;
for(int i = 1; i < pos; i++){
temp = temp->link;
}
new->link = temp->link;
temp->link = new;
}
void deleteFront(){
if(head == NULL){
printf(“List is empty\n”);
return;
}
node *temp = head;
head = temp->link;
printf(“%d is deleted\n”, temp->data);
free(temp);
}
void deleteEnd(){
if(head == NULL){
printf(“List is empty\n”);
return;
}
node *temp = head;
node *prev = NULL;
while(temp->link != NULL){
prev = temp;
temp = temp->link;
}
if(prev != NULL){
prev->link = NULL;
} else {
head = NULL;
}
printf(“%d is deleted\n”, temp->data);
free(temp);
}
void displayList(){
node *temp = head;
printf(“Your data elements are: “);
while(temp != NULL){
printf(“%d “, temp->data);
temp = temp->link;
}
printf(“\n”);
}
int main(){
int option, data;
while(1){
printf(“1. Insert Front\n2. Insert End\n3. Insert at Position\n4. Delete Front\n5. Delete End\n6. Display List\n7. Exit\n”);
printf(“Enter your option: “);
scanf(“%d”, &option);
switch(option){
case 1:
printf(“Enter the value: “);
scanf(“%d”, &data);
insertFront(data);
break;
case 2:
printf(“Enter the value: “);
scanf(“%d”, &data);
insertEnd(data);
break;
case 3:
insertAtPosition();
break;
case 4:
deleteFront();
break;
case 5:
deleteEnd();
break;
case 6:
displayList();
break;
case 7:
exit(0);
default:
printf(“Invalid option\n”);
}
}
return 0;
}
- Implement a C program to create a singly linked list with as many nodes as requested by the user. Read the data that needs to be stored in the nodes of the linked list from the user and display the linked list.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct Node {
int data;
struct Node *next;
} Node;
Node *head = NULL;
Node *memalloc(int value) {
Node *newNode = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if (newNode == NULL) {
printf(“Memory allocation failed”);
exit(0);
}
newNode->data = value;
newNode->next = NULL;
return newNode;
}
void insertAtEnd(int value) {
Node *newNode = memalloc(value);
if (head == NULL) {
head = newNode;
return;
}
Node *temp = head;
while (temp->next != NULL) {
temp = temp->next;
}
temp->next = newNode;
}
void displayList() {
Node *temp = head;
printf(“The elements in the list are: “);
while (temp != NULL) {
printf(“%d “, temp->data);
temp = temp->next;
}X
printf(“\n”);
}
int main() {
int value, nodeCount;
printf(“Enter the number of nodes: “);
scanf(“%d”, &nodeCount);
for (int i = 0; i < nodeCount; i++) {
printf(“Enter the value: “);
scanf(“%d”, &value);
insertAtEnd(value);
}
displayList();
return 0;
}
- Implement a C program to insert a node at any desired position, as read from the user.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef struct Node {
int data;
struct Node *next;
} Node;
Node *head = NULL;
Node *memalloc(int value) {
Node *newNode = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if(newNode == NULL) {
printf(“Memory not allocated”);
exit(1);
}
newNode->data = value;
newNode->next = NULL;
return newNode;
}
void insertAtFront(int value) {
Node *newNode = memalloc(value);
if(head == NULL) {
head = newNode;
return;
}
newNode->next = head;
head = newNode;
}
void insertAtEnd(int value) {
Node *newNode = memalloc(value);
if(head == NULL) {
head = newNode;
return;
}
Node *temp = head;
while(temp->next != NULL) {
temp = temp->next;
}
temp->next = newNode;
}
int countList() {
int count = 0;
Node *temp = head;
while(temp != NULL) {
temp = temp->next;
count++;
}
printf(“The number of elements in the list: %d\n”, count);
return count;
}
void insertAtPosition() {
int position, value;
int listSize = countList();
if(listSize == 0) {
printf(“List is empty\nAdding new node\nEnter the value: “);
scanf(“%d”, &value);
insertAtFront(value);
return;
}
printf(“Enter the position between 0 – %d: “, listSize);
scanf(“%d”, &position);
if(position < 0 || position > listSize) {
printf(“Invalid position or position out of bounds.\n”);
return;
}
printf(“Enter the value: “);
scanf(“%d”, &value);
if(position == 0) {
insertAtFront(value);
return;
}
if(position == listSize) {
insertAtEnd(value);
return;
}
Node *newNode = memalloc(value);
Node *temp = head;
for(int i = 1; i < position; i++) {
temp = temp->next;
}
newNode->next = temp->next;
temp->next = newNode;
}
void displayList() {
Node *temp = head;
printf(“\nYour data elements are: “);
while(temp != NULL) {
printf(“%d “, temp->data);
temp = temp->next;
}
printf(“\n”);
}
int main() {
int option, value;
while(1) {
printf(“1. Insert at Front\n2. Insert at End\n3. Insert at Position\n4. Display List\n5. Exit\n”);
printf(“Enter your option: “);
scanf(“%d”, &option);
switch(option) {
case 1:
printf(“Enter the value: “);
scanf(“%d”, &value);
insertAtFront(value);
system(“cls”);
break;
case 2:
printf(“Enter the value: “);
scanf(“%d”, &value);
insertAtEnd(value);
system(“cls”);
break;
case 3:
insertAtPosition();
system(“cls”);
break;
case 4:
displayList();
break;
case 5:
exit(0);
}
}
return 0;
}